Crypto Options: A Complete Guide (2024)

As cryptocurrencies continue to reshape global finance, new tools and strategies emerge to help investors navigate these volatile markets. One of the most innovative and popular methods for crypto traders is crypto options trading. This blog will explore the mechanics of crypto options, their pros and cons, and the rise of decentralized options platforms, including DOPP, a decentralized exchange (DEX) for options. Finally, we’ll look ahead at how decentralized options could define the future of cryptocurrency trading.
What Are Crypto Options and How Are They Traded?
Crypto options are financial derivatives that enable traders to speculate on the future price movements of cryptocurrency assets like Bitcoin or Ethereum. Similar to traditional options in stock or commodities markets, crypto options give traders the right, but not the obligation, to buy (call option) or sell (put option) a cryptocurrency at a set price (strike price) before a specific expiration date.
Mechanism of Crypto Options
Crypto options operate through a contract between two parties: a buyer and a seller. The buyer of the contract pays a premium for the right to buy or sell the underlying cryptocurrency, while the seller assumes the obligation to fulfill the contract if the buyer exercises the option.
Key elements to understand in crypto options trading include:
- Strike price: The predetermined price at which the buyer can buy or sell the asset.
- Expiration date: The deadline by which the option must be exercised or it becomes worthless.
- Premium: The price paid by the buyer for the option contract.
Buying and Selling Crypto Options
Traders engage in crypto options trading by buying call or put options. If you expect the price of Bitcoin to rise, you might buy a call option, giving you the right to buy Bitcoin at the strike price. Conversely, if you expect Bitcoin’s price to fall, you would buy a put option, allowing you to sell Bitcoin at the predetermined strike price.
On the other hand, selling options (writing options) can also be a profitable strategy. In this case, the seller collects the premium, betting that the buyer will not exercise the option before the expiration date. For example, if you sell a call option and the price of Bitcoin stays below the strike price, you keep the premium without having to sell your Bitcoin holdings.
Pros and Cons of Crypto Options Trading
Pros of Crypto Options Trading
- Profit from both upward and downward price movements: Options allow traders to profit regardless of market direction. Whether you expect the market to rise or fall, call and put options provide a mechanism to capitalize on price movements.
- Leverage with lower capital outlay: Crypto options provide leverage, allowing you to control a larger position in the market with a smaller initial investment compared to buying the asset outright. For example, purchasing a Bitcoin option costs less than buying an entire Bitcoin, while still offering exposure to price movements.
- Hedging against market volatility: Crypto options can serve as a hedge, protecting your portfolio against sudden adverse market movements. For instance, holding a put option on Bitcoin can offset potential losses in a long Bitcoin position if prices drop unexpectedly.
- Flexibility in investment strategies: Options enable a wide range of strategies to suit different market conditions. Traders can engage in conservative hedging strategies or use options for speculative plays with high risk-reward ratios.
Cons of Crypto Options Trading
- High risk due to market volatility: Cryptocurrencies are known for their extreme volatility, and crypto options inherit this characteristic. Price swings can lead to significant profits, but they can also result in rapid and unexpected losses.
- Complex pricing dynamics: Pricing crypto options involves understanding factors such as implied volatility, time decay, and market sentiment. For new traders, these concepts can be difficult to master, increasing the risk of mispriced trades.
- Limited liquidity in some markets: Crypto options markets, especially those involving altcoins, can sometimes lack sufficient liquidity, making it challenging to enter or exit positions at favorable prices.
Key Strategies for Crypto Options Trading
Several options trading strategies are commonly used in crypto markets, each offering a unique risk-reward profile. Below are a few popular strategies:
1. Long Call
A long call gives the buyer the right to buy an asset at the strike price. The profit potential is unlimited, while the loss is capped at the premium paid.Profit = max(0, Price at Expiration - Strike Price) - Premium PaidExample: You buy a call option on Bitcoin with a strike price of $20,000 and a premium of $1,000. If Bitcoin rises to $25,000, your profit is $25,000 - $20,000 - $1,000 = $4,000.

2. Short Put
A short put involves selling a put option, obligating the seller to buy the asset at the strike price if exercised. The maximum profit is the premium received, and the risk is substantial if the asset price falls significantly.Profit = Premium Received - max(0, Strike Price - Price at Expiration)Example: You sell a put option on Ethereum with a strike price of $1,500 and receive a $200 premium. If Ethereum stays above $1,500, you keep the $200. If it drops to $1,300, your loss is $1,500 - $1,300 - $200 = $0.
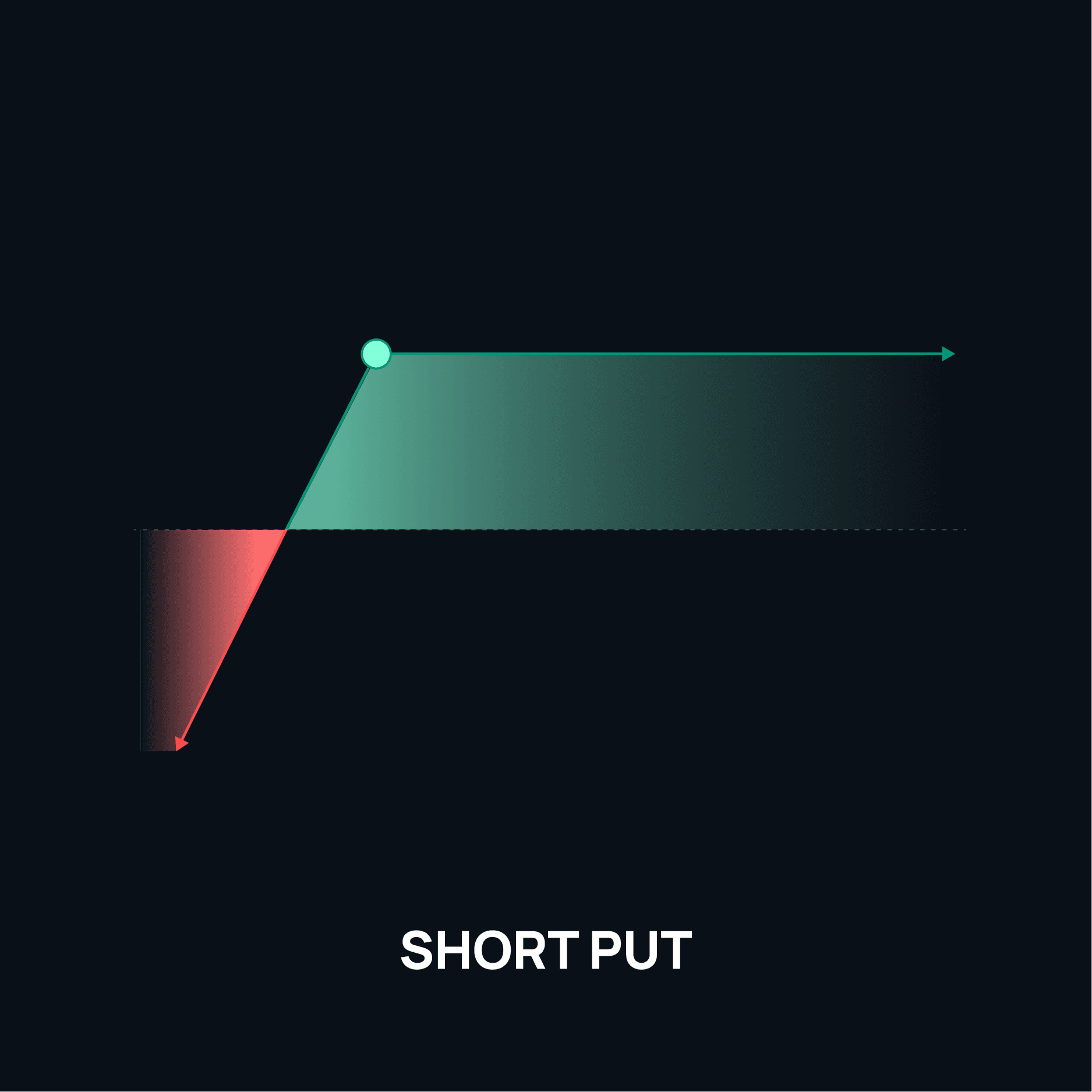
3. Short Call
In a short call, the seller receives a premium and is obligated to sell the asset at the strike price if exercised. The risk is unlimited if the asset price rises.Profit = Premium Received - max(0, Price at Expiration - Strike Price)Example: You sell a call on Bitcoin at a strike price of $30,000 and receive a $500 premium. If Bitcoin rises to $35,000, your loss is $35,000 - $30,000 - $500 = $4,500.

4. Long Put
A long put gives the buyer the right to sell an asset at the strike price. It profits if the asset price drops, and the loss is limited to the premium paid.Profit = max(0, Strike Price - Price at Expiration) - Premium PaidExample: You buy a put on Ethereum with a strike price of $2,000 and pay a $100 premium. If Ethereum falls to $1,500, your profit is $2,000 - $1,500 - $100 = $400.
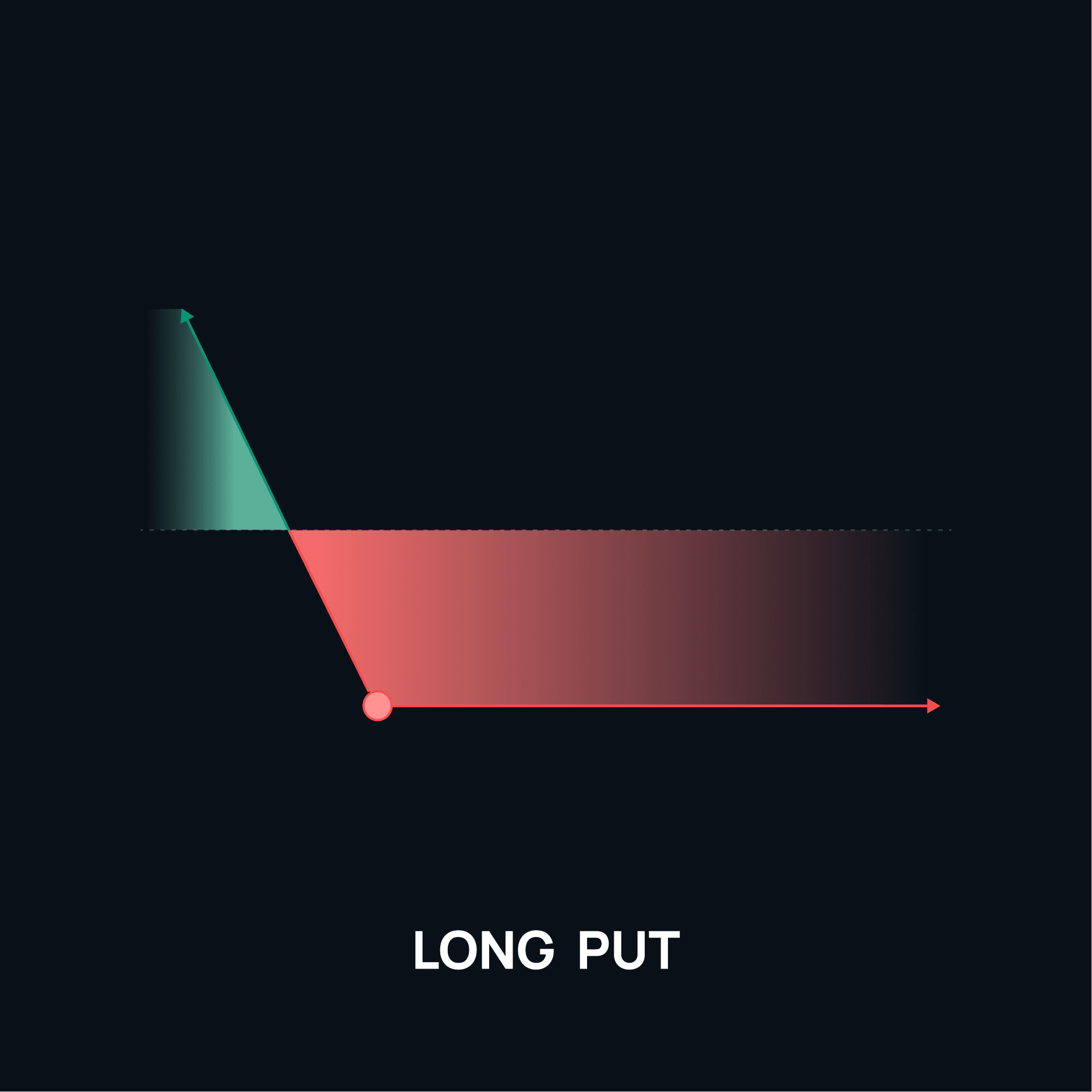
5. Long Perpetual (Perp)
Going long on a perpetual contract allows traders to profit from upward price movements without an expiration date. The profit is based on the difference between the buy and sell price, minus funding fees.Profit = (Price at Exit - Price at Entry) - Funding FeesExample: You go long on a Bitcoin perp at $40,000. If Bitcoin rises to $45,000, your profit is $45,000 - $40,000 = $5,000 (minus any funding fees).
6. Short Perpetual (Perp)
Going short on a perpetual contract allows traders to profit from a decline in the asset's price, without an expiration date.Profit = (Price at Entry - Price at Exit) - Funding FeesExample: You short Ethereum perp at $3,000. If Ethereum drops to $2,500, your profit is $3,000 - $2,500 = $500 (minus funding fees).
7. Put Spread
A put spread involves buying a put at one strike price and selling another at a lower strike price to limit risk and reduce premium costs.Profit = max(0, Higher Strike - Price at Expiration) - max(0, Lower Strike - Price at Expiration) - Net Premium PaidExample: You buy a put with a strike of $50 and sell a put with a strike of $45, paying a net premium of $1. If the asset drops to $46, your profit is $50 - $46 - $1 = $3.
8. Call Spread
A call spread involves buying a call at one strike price and selling another at a higher strike price to limit risk and reduce premium costs.Profit = max(0, Price at Expiration - Lower Strike) - max(0, Price at Expiration - Higher Strike) - Net Premium PaidExample: You buy a call with a strike of $100 and sell a call with a strike of $110, paying a net premium of $2. If the asset rises to $108, your profit is $108 - $100 - $2 = $6.
9. Protective Put
A protective put is used to hedge a long position by buying a put option to limit downside risk.Profit = max(0, Price at Expiration - Initial Asset Price) + max(0, Strike Price - Price at Expiration) - Premium PaidExample: You own 100 shares of stock at $50 and buy a put with a $45 strike price, paying a $1 premium. If the stock drops to $40, your put's profit is $45 - $40 = $5, offsetting the loss on the stock.
10. Long Straddle
A long straddle involves buying both a call and a put at the same strike price, profiting from large price movements in either direction.Profit = max(0, Price at Expiration - Strike Price) + max(0, Strike Price - Price at Expiration) - Premium Paid for Call and PutExample: You buy a call and put on Bitcoin with a strike of $50,000, paying a total premium of $1,000. If Bitcoin rises to $55,000, your profit is $55,000 - $50,000 - $1,000 = $4,000.
11. Long Strangle
A long strangle involves buying a call and put with different strike prices, allowing for large price movements but at a lower cost than a straddle.Profit = max(0, Price at Expiration - Call Strike) + max(0, Put Strike - Price at Expiration) - Premium Paid for BothExample: You buy a call with a strike of $55,000 and a put with a strike of $45,000, paying a $1,500 total premium. If Bitcoin rises to $60,000, your profit is $60,000 - $55,000 - $1,500 = $3,500.
These formulas and examples illustrate how each strategy works, helping traders make informed decisions based on market conditions and personal risk tolerance.
Centralized vs. Decentralized Options Trading Platforms: A Comparison
Centralized Options Trading Platforms
Centralized options trading platforms are traditional exchanges or brokerage services that facilitate options trading through a central authority. These platforms include popular names such as CBOE or Binance.
Key Features:
- Intermediary Control: A centralized platform is run by a company or institution that manages the order books, clearing, and settlement. This intermediary ensures the execution of trades.
- Liquidity: Centralized platforms generally offer high liquidity due to a large number of traders. This allows for better price discovery and easier entry and exit of positions.
- Regulatory Oversight: Most centralized platforms operate under strict regulations and are required to comply with government or financial institution rules. This oversight can provide protection but may also lead to restrictions on who can participate in the market.
- Security Concerns: Funds are typically held in custodial wallets, meaning users don’t have direct control over their assets. This increases the risk of hacks or mismanagement.
- Fees and Costs: Centralized platforms tend to charge higher fees to cover operational costs, including transaction fees, clearing fees, and fees for intermediaries.
- KYC/AML Requirements: Users are often required to provide personal identification and follow Know Your Customer (KYC) and Anti-Money Laundering (AML) protocols to trade on these platforms.
Decentralized Options Trading Platforms
Decentralized options trading platforms, often referred to as DeFi options platforms, operate without a central authority. Instead, they use smart contracts on blockchain technology to manage trades autonomously, with examples like Opynand Hegic.
Key Features:
- No Intermediary: Decentralized platforms eliminate the need for intermediaries. Trades are executed directly between users using smart contracts, enhancing transparency.
- Full Asset Control: Users maintain full control of their assets throughout the trade. Instead of relying on a platform to custody funds, decentralized options use non-custodial wallets, ensuring users’ assets are always in their control.
- Global Accessibility: Decentralized platforms are open to anyone with a cryptocurrency wallet and internet access. There are no regional restrictions or heavy regulatory hurdles, making them accessible globally.
- Lower Fees: By eliminating intermediaries, decentralized platforms often reduce fees associated with trading, clearing, and settlements. Transaction fees are mostly limited to network gas fees.
- Security via Blockchain: Decentralized platforms use blockchain for transparency, ensuring every trade and transaction is publicly verifiable. The risk of hacking is minimized as users hold their own private keys, though the platform’s smart contract code must be secure.
- No KYC Requirements: Unlike centralized exchanges, decentralized platforms do not require personal information from users. This enhances privacy but can lead to potential regulatory challenges in the future.
Key Differences
Feature
Centralized Platform
Decentralized Platform
Control
Managed by a central authority
No intermediaries, managed by smart contracts
User Control of Funds
Funds held in custodial wallets
Users retain control of their assets
Liquidity
Generally higher due to larger user bases
Liquidity may be lower depending on the platform
Regulation
Highly regulated, requires KYC/AML
No KYC, open to global users, fewer regulatory barriers
Security
Vulnerable to hacking, as funds are held by the exchange
Enhanced security due to non-custodial wallets
Fees
Higher due to operational costs and intermediaries
Lower, with only gas fees for network transactions
Transparency
Limited to what the exchange reveals
Fully transparent, all transactions on the blockchain
Accessibility
May be restricted in certain regions or require heavy compliance
Accessible to anyone with a crypto wallet worldwide
Why Decentralized Options Trading Platforms Are the Future
The growing popularity of decentralized options platforms points to several advantages that are shaping the future of trading. Here’s why decentralized platforms are becoming the go-to solution:
- User Empowerment: The core benefit of decentralized platforms is that users have full control over their funds and assets at all times. This minimizes the risk of hacking or mismanagement, and allows users to participate in trades without needing to trust a central authority.
- Lower Fees: With no intermediaries and fewer operational costs, decentralized platforms offer more cost-effective options trading. This is especially important for smaller traders who are seeking to minimize costs and maximize profits.
- Global Reach and Accessibility: Decentralized platforms open up options trading to anyone, regardless of geographical location or financial status. This democratizes access and creates a more inclusive financial system, unlike centralized platforms that require KYC and may exclude users from certain regions.
- Blockchain Transparency: Every transaction on a decentralized platform is recorded on the blockchain, providing full transparency. This trustless system ensures fairness and accuracy, removing any possibility of manipulation by the platform operator.
- Innovation and Flexibility: Decentralized platforms are evolving quickly, allowing for innovative features like custom-built financial products and decentralized governance. As blockchain technology progresses, decentralized platforms can continue to push the boundaries of financial innovation, offering traders new opportunities.
Decentralized options trading platforms represent the future of the options market. As the world shifts towards decentralized finance, these platforms offer significant advantages over their centralized counterparts—such as user control, lower fees, global accessibility, and enhanced transparency. With increasing adoption and continuous innovation in DeFi, decentralized options platforms are well-positioned to become the standard for traders seeking freedom, security, and efficiency in the world of options trading.
Decentralized Options Platforms (DOPP): The Future of Crypto Options
As the cryptocurrency ecosystem continues to grow, decentralized finance (DeFi) is transforming how financial products are created and traded. One of the most promising innovations is the rise of Decentralized Options Platforms (DOPP). These platforms enable users to trade options without intermediaries, utilizing blockchain technology and smart contracts to manage transactions.
How DOPP Works
In a traditional financial system, options trading often takes place on centralized exchanges, requiring intermediaries to facilitate trades. However, decentralized options platforms eliminate these middlemen by using smart contracts that automatically execute trades based on predefined conditions.
Here’s how it works:
- Smart Contracts: All trades are governed by smart contracts, which ensure transparency, security, and automation. This reduces the risk of fraud and eliminates the need to trust a central authority.
- User Control: With DOPP, users retain full control of their funds throughout the trading process. There’s no need to transfer assets to a third party, as trades are executed directly on the blockchain.
- Orderbooks: DOPP's Unique Selling Proposition (USP) lies in its order book-based decentralized options trading model, a significant departure from the more common liquidity pool-based DeFi platforms. This gives DOPP several key advantages:
- Precision and Flexibility: By using an order book, DOPP allows traders to set their desired prices for options contracts, providing greater control and flexibility. Unlike liquidity pool-based platforms where prices are often determined algorithmically, DOPP offers users the ability to directly negotiate the price, ensuring more accurate and efficient price discovery.
- Transparency and Decentralization: DOPP operates on the blockchain, ensuring full transparency and decentralization of the options trading process. Traders can trust that every order, trade, and contract execution is recorded immutably on the blockchain without the need for intermediaries, creating a more trustless and secure trading environment.
- Non-Custodial and Secure: DOPP allows traders to maintain control over their funds at all times through non-custodial wallets. This eliminates the risk of hacking or mismanagement associated with centralized exchanges, ensuring that users' assets are secure throughout the trading process.
DOPP aims to create a decentralized options trading platform that combines the simplicity and security of DeFi with the power and functionality of centralized exchanges (CEX). By utilizing an order book-based model, DOPP provides a familiar trading experience for seasoned traders accustomed to centralized platforms while offering the advantages of decentralization. This unique approach allows traders to place limit and market orders, set specific prices, and manage their strategies with precision, making DOPP a seamless bridge between traditional trading tools and the decentralized world.
Despite its advanced features, DOPP is designed to be simple and user-friendly, ensuring that even complex options trading can be executed effortlessly. The intuitive interface and powerful tools allow experienced traders to leverage their knowledge and skills without being bogged down by unnecessary complications. With DOPP, users get the best of both worlds: the sophistication and precision of a CEX-like trading experience, combined with the decentralization, security, and transparency that DeFi offers.
Advantages of Decentralized Options Trading
- Transparency and Trust: All trades on decentralized platforms are visible on the blockchain, providing full transparency. The use of smart contracts ensures that trades are executed fairly and automatically, without the need for human intervention.
- Lower Fees: Decentralized options platforms often have lower fees compared to centralized exchanges. This is because there are no intermediaries taking a cut of each trade, and the use of blockchain reduces operational costs.
- Global Accessibility: Anyone with an internet connection and a crypto wallet can access decentralized options platforms. There are no geographic restrictions or gatekeepers, making options trading accessible to a wider range of users globally.
- Security: Funds in decentralized platforms are stored in smart contracts, reducing the risk of hacking or theft associated with centralized exchanges, which store funds in centralized wallets.
Challenges Facing Decentralized Options
Despite the promise of decentralized options platforms, several challenges remain:
- Liquidity Issues: Some decentralized options platforms may lack liquidity, which can make it difficult for traders to find counterparts for their trades. As a result, slippage and wide bid-ask spreads can affect trade execution.
- Complexity for New Users: The technical requirements of decentralized platforms, including setting up wallets and interacting with smart contracts, can be daunting for novice users.
- Regulatory Uncertainty: As decentralized finance evolves, so does the regulatory landscape. There is still uncertainty regarding how different jurisdictions will treat decentralized options platforms, and regulatory changes could impact their future growth.
Conclusion: The Future of Crypto Options
Crypto options trading is fast becoming an integral part of the cryptocurrency landscape, offering investors a flexible and sophisticated tool for hedging and speculation. While traditional options markets still dominate, the rise of decentralized options platforms like DOPP represents the next stage in the evolution of crypto derivatives.
Decentralized options platforms offer the benefits of transparency, security, lower fees, and global accessibility, making them an attractive alternative to centralized exchanges. However, challenges such as liquidity constraints, user complexity, and regulatory uncertainty must be addressed for decentralized options to reach their full potential.
As the cryptocurrency market continues to mature and the decentralized finance ecosystem grows, crypto options trading—particularly on decentralized platforms—will play a pivotal role in the future of digital asset markets. For traders and investors, mastering the nuances of crypto options today could unlock significant opportunities in the years to come.
← Return home