A Comprehensive Guide to Decentralized Prediction Markets

In an age where blockchain technology is reshaping traditional finance, prediction markets have emerged as one of the most exciting and innovative applications. From forecasting election results to predicting weather patterns or cryptocurrency prices, prediction markets leverage the collective intelligence of participants to forecast real-world events. This guide will delve into the workings of prediction markets, explore their decentralized variations, and discuss their implications in the finance and technology world. Whether you're a novice or an experienced trader, this article will provide a comprehensive understanding of prediction markets and their growing influence.
What Are Prediction Markets?
At their core, **prediction markets** are platforms where users can trade contracts that represent the possible outcomes of future events. These contracts function similarly to financial derivatives, where the price fluctuates based on the perceived likelihood of the event occurring.
Participants in prediction markets buy and sell these contracts in an open market, with prices adjusting in real-time based on supply and demand. The more likely an outcome is perceived to be, the higher its contract price, and conversely, the less likely an outcome, the lower its price. Once the event concludes, the market "settles," and traders holding contracts for the correct outcome receive a payout.
Prediction markets differ from traditional betting or futures markets because they aggregate information from a large group of participants, resulting in highly accurate predictions. The collective intelligence of the market often outperforms individual experts or polls, making prediction markets an effective tool for forecasting.
How Prediction Markets Work
The mechanics of prediction markets are straightforward. Let's break down the process:
1. Creation of a Market: A prediction market is established for a specific event. For example, a market could be created to predict the outcome of the next U.S. presidential election, with contracts available for each potential winner (e.g., Candidate A, Candidate B).
2. Buying and Selling Contracts: Users buy contracts for the outcome they believe will happen. These contracts represent different event outcomes (e.g., a win for Candidate A or Candidate B). Each contract is priced based on the likelihood of that outcome, as perceived by the market participants. For example, if Candidate A is favored to win, their contract price may be higher.
3. Price Adjustments: As more people buy or sell contracts for a particular outcome, the price adjusts. This pricing mechanism reflects the collective opinion of the market participants on the likelihood of the event's outcomes.
4. Market Settlement: When the event occurs, the prediction market settles. Traders holding contracts for the correct outcome receive payouts based on the contract price at the time of purchase. Those who bought contracts early for the correct outcome typically earn higher returns than those who purchased later.
Prediction markets can be used for various types of events, including political elections, sports games, financial markets, and even weather forecasts.
Applications of Prediction Markets
Prediction markets have a wide range of applications, including:
Political Elections: During elections, prediction markets can forecast outcomes based on real-time trading data. For example, in the 2016 U.S. presidential election, prediction markets accurately predicted Donald Trump's victory, despite traditional polls showing otherwise.
Sports Events: Prediction markets allow users to speculate on the outcomes of sports events such as the Super Bowl. Traders analyze team statistics, player performance, and other factors to buy contracts for the team they believe will win.
Stock Market: Financial markets can benefit from prediction markets as well. Traders can predict the future price of a particular stock or asset based on economic indicators, company performance, or market trends.
Cryptocurrency Prices: In the volatile world of cryptocurrency, prediction markets can be used to speculate on future prices of assets like Bitcoin and Ethereum. Traders use market data, technical analysis, and sentiment to predict price movements.
Weather Events: Prediction markets can even forecast natural events such as hurricanes or tornadoes. By aggregating data from weather models, historical patterns, and expert forecasts, these markets can provide insights into the likelihood of specific weather outcomes.
Decentralized Prediction Markets: The DeFi Revolution
In recent years, **decentralized prediction markets** have gained popularity, offering several advantages over traditional, centralized platforms. These markets are built on blockchain technology and are a key part of the broader decentralized finance (DeFi) movement.
Decentralized prediction markets eliminate the need for a central authority or intermediary to manage the platform. Instead, they use **smart contracts** to automate the process of creating markets, executing trades, and settling outcomes. This offers several benefits, including enhanced transparency, lower fees, and increased privacy.
Key Features of Decentralized Prediction Markets
Smart Contracts: In decentralized markets, smart contracts are used to manage every aspect of the market, from the creation of events to the settlement of outcomes. These contracts run automatically on the blockchain, reducing the need for human intervention.
Privacy and Security: Since decentralized markets are powered by blockchain technology, participants can trade anonymously using digital assets without connecting their bank accounts or personal information to the platform. This enhances privacy and security for users.
Global Participation: Decentralized prediction markets are accessible globally, allowing participants from all over the world to engage. This opens up a broader pool of participants and ensures more liquidity and diversity in market opinions.
Lower Fees: Without the need for intermediaries or centralized platforms to take a cut, decentralized prediction markets often have lower transaction fees, making them more cost-effective for participants.
Quadratic Voting: Some decentralized platforms incorporate **quadratic voting**, which allows users to allocate more votes or influence toward an outcome they feel strongly about. The quadratic formula ensures that the cost of additional votes increases exponentially, preventing any one participant from dominating the market with excessive funds.
How Decentralized Prediction Markets Work
Similar to traditional markets, decentralized prediction markets allow users to buy and sell contracts representing different outcomes of future events. However, the entire process is automated and trustless, thanks to blockchain technology and smart contracts. Here's how it works:
Market Creation: Anyone can create a new market for an event by deploying a smart contract. This could be a political election, a sports event, or even something more niche, like the release of a new video game trailer.
Buying and Selling Contracts: Participants purchase contracts using cryptocurrencies such as Ethereum or stablecoins like Dai. As users buy and sell contracts, the smart contract automatically adjusts the prices based on demand and perceived likelihood.
Automated Settlement: Once the event concludes, the market automatically settles through the smart contract, distributing payouts to those who predicted the correct outcome.
Decentralization Benefits: Since there’s no central authority, these markets are less susceptible to censorship, bias, or manipulation. Additionally, decentralized markets tend to be more global and liquid, as participants from any country can easily access them.
Polymarket: A Leading Example of Decentralized Prediction Markets
One of the most notable decentralized prediction markets is **Polymarket**. Built on blockchain technology, Polymarket enables users to bet on a wide variety of real-world events, ranging from political elections to cryptocurrency price movements. Polymarket has grown rapidly, with a record $473 million in trading volume in August 2023 and a 40% month-over-month growth in active traders.
Decentralized Prediction Markets offers several advantages over traditional, centralized prediction platforms:
No intermediaries: Polymarket operates without intermediaries, meaning lower fees for participants.
Enhanced privacy: Participants use cryptocurrencies, so they don’t need to connect traditional bank accounts or debit cards.
Global reach: Polymarket allows global participation, ensuring more liquidity and diversity in opinions.
Real-time pricing: The platform uses blockchain to ensure that the prices of contracts adjust in real-time based on market activity.
While decentralized markets offer many benefits, they also face certain challenges. For instance, the ability to create markets for any event can lead to potentially controversial or illegal activities, prompting the need for regulation in some jurisdictions. We will discuss it later.
Key Advantages of Decentralized Prediction Markets
Transparency and Trust
One of the most significant advantages of decentralized prediction markets is transparency. Traditional prediction markets often rely on a central authority to manage transactions and settle disputes. In contrast, decentralized prediction markets are built on blockchain technology, which ensures that every transaction, contract, and market event is publicly recorded on an immutable ledger.
Since all transactions are visible on the blockchain, users can audit the platform, track outcomes, and verify that markets are being operated fairly. This transparency builds trust among participants, as they no longer need to rely on a central party to ensure the integrity of the market. Smart contracts, which automate and enforce market rules, further enhance trust by eliminating human error or bias.
Global Accessibility
Decentralized prediction markets are open to anyone with internet access and a cryptocurrency wallet, making them globally accessible. This is in stark contrast to centralized markets, which may limit participation based on geographic location, government regulations, or membership requirements.
Global accessibility increases the number of participants in the market, leading to a more diverse range of opinions and, ultimately, more accurate predictions. It also democratizes access to financial markets, allowing people from underbanked regions or countries with limited financial infrastructure to participate in global economic activities.
Lower Fees
Another major advantage of decentralized prediction markets is the potential for lower fees. Centralized platforms often charge substantial fees to cover the costs of operating servers, employing staff, and managing transactions. Additionally, centralized systems often act as intermediaries, taking a cut of the profits for providing their services.
In decentralized markets, smart contracts handle these tasks automatically, eliminating the need for intermediaries and significantly reducing operational costs. As a result, participants benefit from lower transaction fees, allowing them to keep more of their profits. This cost-efficiency makes decentralized platforms an attractive option for traders, especially those who engage in high-frequency trading or small-scale transactions.
Enhanced Privacy
Privacy is a growing concern for participants in centralized markets, where users are often required to provide personal information, such as bank account details or identity verification. This information can be vulnerable to hacking, data breaches, or misuse by the platform.
Decentralized prediction markets solve this problem by allowing participants to remain anonymous. Since transactions are conducted using cryptocurrencies, there is no need to provide personal information to participate. This enhanced privacyappeals to users who value their security and personal data and want to avoid the risks associated with centralized financial systems.
No Intermediaries
Traditional financial markets and centralized prediction platforms rely on intermediaries to manage transactions, validate market outcomes, and resolve disputes. These intermediaries can slow down the process, introduce potential errors, and impose high fees. Additionally, they centralize power, meaning users must trust a single entity to act in good faith.
In decentralized prediction markets, smart contracts replace intermediaries. These contracts are self-executing and automatically enforce the terms of the market without the need for human intervention. This automation increases efficiency and ensures that transactions and outcomes are processed fairly, quickly, and without bias. By removing intermediaries, decentralized prediction markets also reduce costs and make the system more accessible to a broader audience.
Global Participation and Liquidity
The decentralized nature of prediction markets makes them inherently global, allowing participants from any part of the world to join. This results in larger markets with more participants, which in turn improves liquidity.
In prediction markets, liquidity refers to the ease with which participants can buy or sell contracts without causing significant price fluctuations. A market with high liquidity ensures that traders can enter and exit positions easily, reducing the risk of price manipulation by a small group of participants. Decentralized prediction markets tend to have more liquidity because they attract a global user base, leading to more accurate price discovery and a fairer market overall.
Incentive-Driven Accuracy
Prediction markets are inherently incentive-driven. Participants are financially motivated to make accurate predictions because correct predictions result in payouts. This creates a strong incentive for participants to gather information, analyze data, and make well-informed decisions. In contrast, other forecasting methods, such as opinion polls or expert predictions, do not offer the same level of financial motivation.
The combination of global participation and financial incentives in decentralized prediction markets results in more accurate predictions. As more people with diverse perspectives participate, the market price of a contract reflects the collective wisdom of the crowd, often providing more accurate forecasts than individual experts or traditional methods.
Censorship Resistance
One of the core principles of blockchain technology is censorship resistance. Decentralized prediction markets operate on blockchain networks, which are distributed and decentralized, meaning there is no single entity that can control, censor, or shut down the platform.
In some regions, centralized prediction markets may be subject to government regulations, bans, or manipulation. However, decentralized platforms operate outside the control of any one entity, making it difficult for governments or other organizations to censor them. This ensures that participants can freely trade contracts and express their opinions without fear of censorship or political interference.
Integration with DeFi Ecosystem
Decentralized prediction markets are part of the larger decentralized finance (DeFi) ecosystem, which includes lending platforms, decentralized exchanges, and other financial products built on blockchain technology. This integration opens up new opportunities for prediction markets to collaborate with other DeFi applications, providing enhanced liquidity, access to borrowing and lending markets, and even the potential for staking rewards.
For example, participants could use their earnings from prediction markets as collateral for loans on DeFi platforms, creating a seamless financial ecosystem where assets can be transferred and utilized across various applications. This interoperability enhances the utility of decentralized prediction markets, making them more versatile and valuable to participants.
Challenges and Risks of Prediction Markets
While prediction markets offer significant advantages, they are not without challenges. Some of the key risks and concerns include:
Market Volatility
Cryptocurrency markets are notoriously volatile, and decentralized prediction markets are no exception. The value of contracts in these markets is often tied to cryptocurrencies like Ethereum or stablecoins, which can fluctuate significantly. This volatility can create large price swings, making it challenging for participants to predict outcomes accurately and manage risk.
In addition to crypto market fluctuations, the nature of the event being predicted can also contribute to volatility. As new information emerges, the market may experience sudden price adjustments, creating further uncertainty for traders.
Liquidity Issues
One of the critical challenges for decentralized prediction markets is liquidity. Liquidity refers to the ability to buy or sell contracts quickly without affecting the market price. In markets with low liquidity, participants may struggle to find buyers or sellers, leading to price distortions and inefficiencies.
Low liquidity can result in higher spreads between buying and selling prices, making it more difficult for participants to enter or exit positions at favorable prices. Additionally, in illiquid markets, a small number of participants may disproportionately influence contract prices, skewing the market's collective intelligence.
Regulatory Issues
The regulatory landscape for decentralized prediction markets remains uncertain and evolving. In many jurisdictions, prediction markets are often equated with gambling, leading to restrictions or outright bans on their use. The decentralized nature of these platforms complicates enforcement, as they often operate without a centralized entity that can be held accountable.
As governments and regulatory bodies work to define the legal status of blockchain-based prediction markets, participants may face concerns over the legitimacy of specific platforms. There is also the risk of future regulatory crackdowns, which could limit or even shut down access to certain decentralized prediction markets in various regions.
Feeding of False Information
Decentralized prediction markets rely on external sources of information, called oracles, to verify the outcomes of events. Oracles feed data into the blockchain, allowing smart contracts to determine the winners and losers in a prediction market. However, oracles are susceptible to manipulation, hacking, or other malicious attacks.
If an oracle is compromised, it may feed incorrect or false information into the system, leading to erroneous market outcomes. This could result in traders receiving payouts for incorrect predictions, undermining trust in the platform and causing financial losses for participants who correctly predicted the event.
Technological Problems
Decentralized prediction markets operate using smart contracts, which are self-executing contracts written in code. While smart contracts are designed to automate and secure market transactions, they are only as reliable as the code they are built on. Any flaw, bug, or loophole in the code can lead to unintended consequences, including financial losses for participants.
For example, if a smart contract has a vulnerability, hackers may exploit it to manipulate the market, steal funds, or disrupt trading. These technological risks are inherent in blockchain projects and can pose significant threats to decentralized prediction markets if not carefully managed.
The Future of Decentralized Prediction Markets
Despite the risks and challenges, the future of decentralized prediction markets looks promising. As blockchain technology continues to mature, several trends and developments will likely shape the evolution of these platforms:
Improved Oracle Systems
To mitigate the risk of false information, decentralized prediction markets will likely focus on improving oracle systems. New solutions such as multi-signature oracles, where multiple sources must agree on an outcome before it is fed into the blockchain, are already in development. These systems can reduce the chances of manipulation or malicious activity.
Moreover, decentralized oracle networks like Chainlink are gaining popularity, ensuring that no single entity controls the flow of information. Such advancements will strengthen the reliability and accuracy of prediction markets.
Enhanced Smart Contract Security
As blockchain developers gain more experience with smart contract technology, security protocols will improve. Audits, code reviews, and bug bounty programs are becoming standard practices for decentralized platforms, helping to identify and fix vulnerabilities before they are exploited. In the future, we can expect more secure and reliable smart contracts that minimize technological risks for prediction market users.
Increased Liquidity and Participation
One of the most significant barriers to decentralized prediction markets is liquidity. As these markets grow and become more popular, increased participation will naturally lead to better liquidity, allowing for more accurate price discovery and less price manipulation.
Moreover, as decentralized finance (DeFi) continues to expand, there will likely be more integration between prediction markets and other DeFi applications. This integration could unlock new liquidity sources, such as lending platforms or liquidity pools, further enhancing market efficiency.
Regulatory Clarity
Although regulatory uncertainty remains a significant challenge, governments and regulatory bodies are beginning to address decentralized platforms. Over time, clearer regulations may emerge, providing a legal framework for decentralized prediction markets to operate within.
Regulation may also lead to more investor confidence, as potential participants will have greater certainty about the legality and safety of using these platforms. However, striking the right balance between regulation and decentralization will be crucial to preserving the core benefits of decentralized markets.
Mainstream Adoption
As awareness of decentralized prediction markets grows and technical challenges are addressed, there is significant potential for mainstream adoption. Prediction markets could expand into more areas, such as corporate decision-making, economic forecasting, and social initiatives. With global access, transparency, and incentive-driven participation, decentralized prediction markets could transform how we make predictions and gather information about future events.
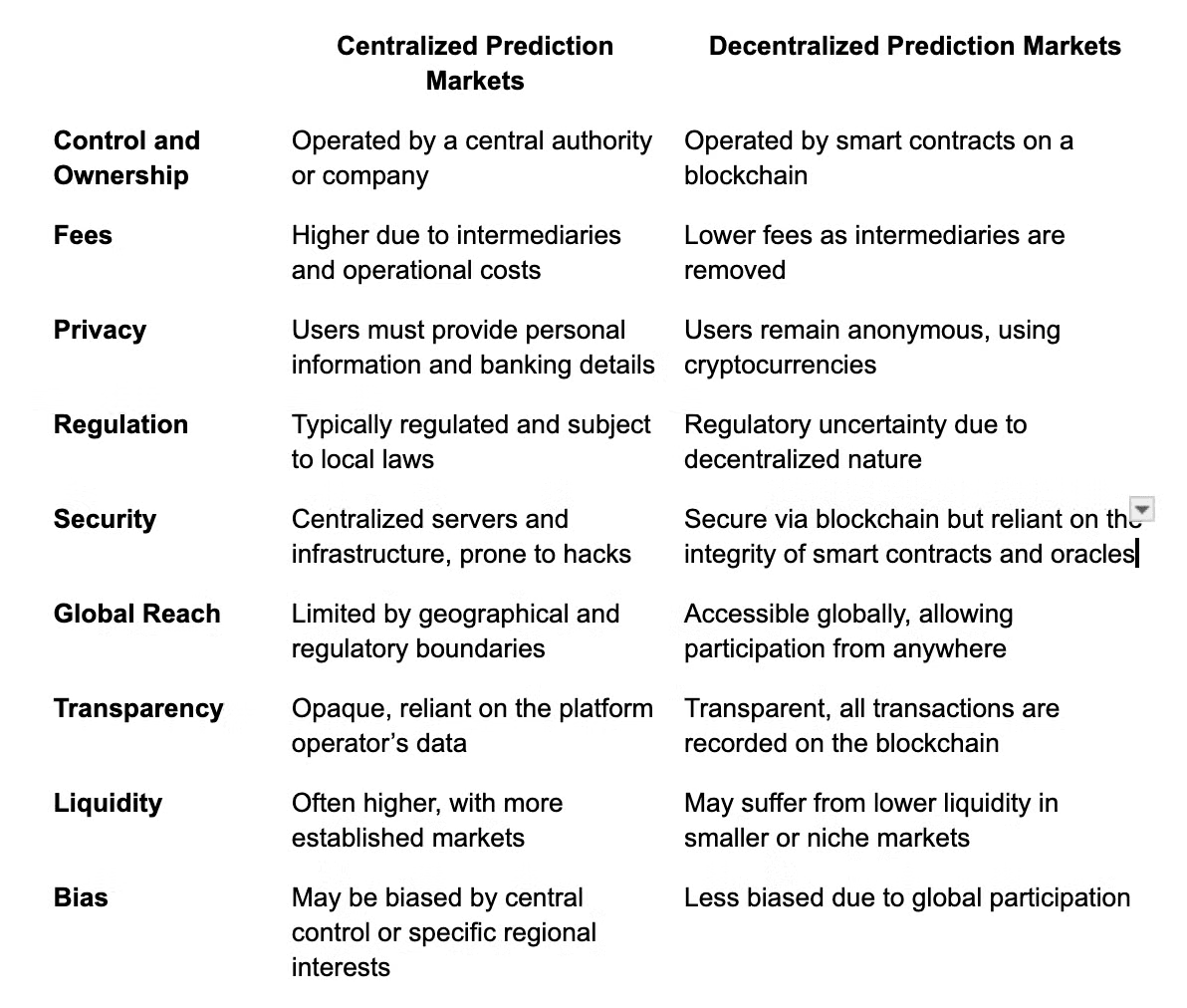
Conclusion
Decentralized prediction markets represent a revolutionary innovation in forecasting real-world events by leveraging blockchain technology. Despite their potential, they are not without risks—market volatility, liquidity issues, regulatory uncertainty, oracle reliability, and technological problems all pose challenges for participants and developers alike.
By comparing centralized and decentralized prediction markets, we see that each has its strengths and weaknesses. While centralized markets offer stability and regulatory oversight, decentralized markets offer privacy, transparency, and global access. The future of decentralized prediction markets will likely depend on technological advancements, improved security, regulatory clarity, and increased liquidity.
With the right innovations and solutions, decentralized prediction markets have the potential to become a mainstream tool for forecasting and decision-making, reshaping industries and providing new ways to tap into the collective wisdom of global participants.
← Return home